Nowadays, we are immersed in a global digitization that has caused a huge change in all areas of our daily life. The adoption of technology in social and business environments brings many transdisciplinary benefits. On the one hand, in the social environment, we are able to extend knowledge without limits, accelerate our productivity because of a multitude of technological tools, improve our communication using efficient tools or applications, increase our creativity by having new exploration capabilities, and easily collaborate to achieve a common goal (among others). On the other hand, in the business environment, the application of technology provides a cost reduction by optimizing resources, an increased productivity by achieving more agile processes and, an increased engagement with customers by streamlining the response and real time direct contact. For an organization, these benefits become a higher turnover.
Nonetheless, the negative impacts that this adoption of technological advances must be considered. Digitisation requires investment in any field, it never ends because technology is changing and improving rapidly and it is necessary to adapt and learn to work with it. But, one of the critical points that cannot be underestimated is that digitisation requires the interconnection of systems and devices to the Internet, a factor that can expose sensitive personal and organizational information. To successfully achieve a global digital transformation, it is important that the systems provide privacy, reliability and security. Before COVID-19, it was already important to protect these systems; multiple daily cyber-attacks put companies and people at risk. But the pandemic has caused an acceleration of the digital transformation that, now more than ever, requires the application of cybersecurity to persevere.
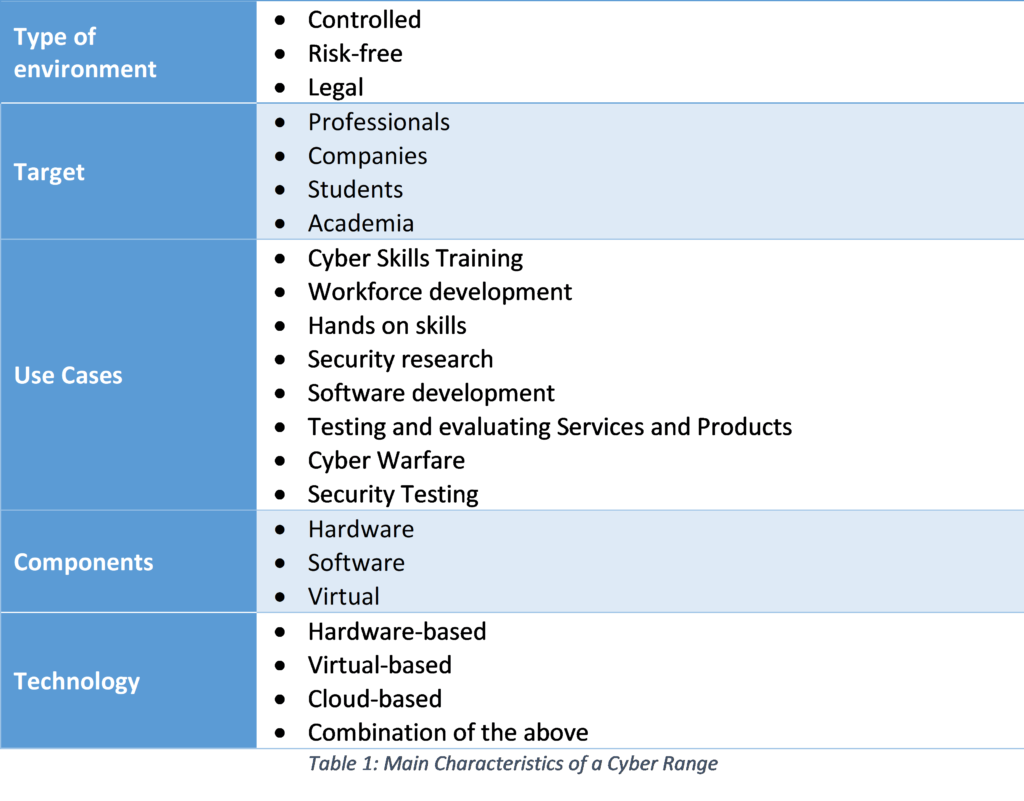
And here lies the opportunity and the problem: There is a global raising demand for cyber professionals and there is a skills gap to be covered to prepare professionals for the digitalisation of current and future systems. A complete and competent training can cover these needs. Furthermore, it should be focused not only on newcomers to the sector, but also on updating the knowledge of senior profiles who need to catch up. There are different ways of transmitting knowledge, different types of learning; from traditional methods based on lectures to the application of active methodologies where the students cooperate in their learning. In recent years, the use of Cyber Ranges has proliferated.
The concept of a Cyber Range can be quite difficult to comprehend as many sources define it in a different manner [1-4]. In some cases, this concept is linked with a professional development solely while others put more emphasis on its educational side. After evaluating various definitions from both government agencies and companies in the sector, we can define a Cyber Range as follows:
A Cyber Range is a simulated environment where situational operations training, testing, research, and educational development can be performed. Therefore, the scope of Cyber Ranges is not only limited to organizations and professionals but also students and educational entities.